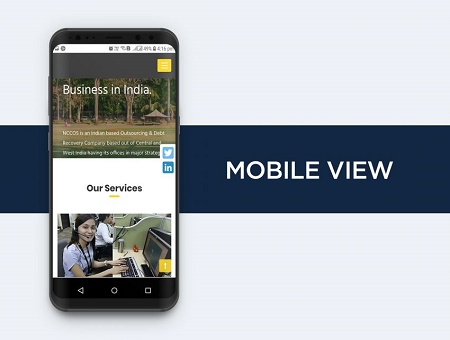
Node.js is an open-source, cross-platform JavaScript runtime environment that allows developers to run JavaScript code outside of a web browser. It is built on Chrome’s V8 JavaScript engine and is widely used for building fast and scalable network applications.
Node.js uses an event-driven, non-blocking I/O model, which makes it lightweight and efficient. It is particularly suited for building real-time applications such as chat apps, streaming services, and APIs.
With its vast package ecosystem (npm – Node Package Manager), Node.js provides developers with thousands of libraries and tools to speed up development and add powerful functionality.
Here's a breakdown of what Node.js is and how it works:
- JavaScript Everywhere: Node.js enables developers to use JavaScript for both frontend and backend, unifying web application development under a single language.
- Non-Blocking I/O: Node.js uses asynchronous, event-driven programming, allowing it to handle thousands of concurrent connections efficiently without blocking operations.
- Fast Performance: Powered by Google’s V8 engine, Node.js executes JavaScript code at high speed, making it great for data-intensive applications.
- Open Source: Node.js is free to use and supported by a huge developer community, providing open-source modules and frameworks to extend its capabilities.
- Cross-Platform: Node.js runs on Windows, Linux, and macOS, making it highly versatile for different environments and servers.
- Rich Ecosystem: npm (Node Package Manager) is the world’s largest software registry, offering millions of packages that simplify development.
Node.js is widely used for creating APIs, microservices, and full-stack applications, making it one of the most important technologies for modern web development.